“A large number of countries in Africa, the Middle East, and Asia are under serious freshwater stress and are facing a projected increase in water scarcity well into 2025”.
Water is the essence of life. In many coastal regions of India, there is scarcity of drinking water. Even when water is available, it is usually through contaminated sources such as lakes or water from desalination plants that only reduce the salt level to acceptable limits. The energy cost for desalination plants are also a major concern.
Proposed Solution:
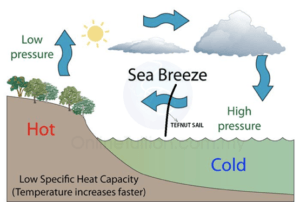
Solar energy is probably one of the cleanest forms of energy. As a result of sun’s radiation, everyday seawater evaporates to create a moisture rich high pressure zone at coastal regions. Tefnut freshwater(TFW) aims to utilize the pressure difference created across the sea and land mass by using a venturi and dehumidifier to generate clean drinking water. The design is scalable and sustainable. Higher levels of energy efficiency is also achieved over existing desalination plants and dehumidifiers.
The TFW is a device installed in seas near tropical deserts. It works for 8-12 hours a day when the sun is creating a sea breeze by heating the air above the waters — so that, importantly, the breeze has maximum water carrying capacity. This breeze is collected by a very large sail and cold squeezed into freshwater. Most deserts are near seas, and this device is installed in deserts, the aim – reforestation

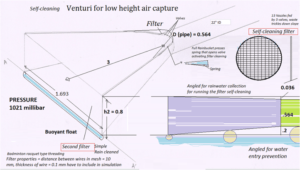
Business Model:
Tefnut freshwater aims to create large scale water generators across both industrial and residential domains. For the business model, monetization strategies are separated into Commercial, Industrial and non-commercial.
Commercial TFW generators:
Commercial TFW generators would be used to provide water to urban households and small businesses. The commercial version of the plants would be sold as a manufacturing unit to a business owner who has either a need to supply drinking water to an urban residential colony or small businesses. The distribution post coastal region would be handled by the client.
Industrial TFW generators:
Industrial plants would be sold to manufacturing units. Typically these would be larger in size and custom designed to help alleviate reliance on source of fresh water such a lakes and rivers.
Non-commercial TFW generators:
Non-commercial TWF generators would be installed in regions that are facing serious shortage of drinking water. These plants would be maintained either by TFW teams or in partnership with government agencies. Alternate clients for non-commercial plants would be large corporates under the Corporate social responsibility plans.

